Grub Bugs Life: Understanding and Managing Lawn Grubs
Lawn grubs, often referred to as “grub bugs,” are a common nuisance for homeowners striving for a pristine, green lawn. These subterranean pests can wreak havoc on your turf, turning lush landscapes into patchy, brown eyesores. Understanding the grub bugs life cycle, identifying their presence, and implementing effective management strategies are crucial for maintaining a healthy and vibrant lawn. This article delves into the world of lawn grubs, providing practical insights for dealing with these unwanted guests.
What are Grub Bugs?
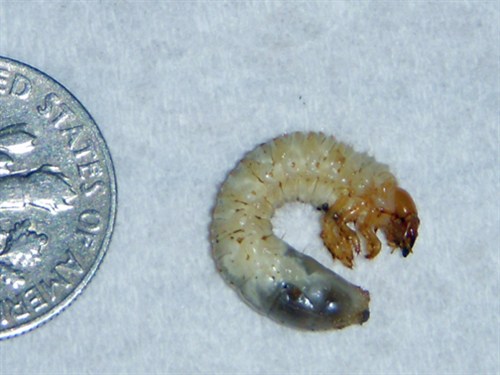
“Grub bugs” is a general term that typically refers to the larvae of various beetle species, primarily Japanese beetles, European chafers, and masked chafers. These creamy white, C-shaped larvae feed on the roots of grasses, causing significant damage beneath the surface. While a few grubs might not pose a major threat, a large infestation can quickly decimate a lawn’s root system, leading to widespread browning and dieback.
Identifying Grub Damage
Recognizing the signs of a grub infestation early can help prevent extensive damage. Common indicators include:
- Brown, Spongy Patches: Affected areas will often appear brown and feel spongy underfoot, as the roots are no longer anchoring the grass.
- Loose Turf: You can easily lift up the turf in infested areas, as the grubs have severed the root system.
- Increased Bird and Animal Activity: Birds, skunks, raccoons, and other animals may start digging in your lawn to feed on the grubs.
- Visible Grubs: If you suspect a grub problem, dig up a square foot of turf to a depth of 2-3 inches and examine the soil for the presence of grubs.
The Grub Bugs Life Cycle
Understanding the grub bugs life cycle is essential for effective management. Most grub species follow a similar pattern:
- Egg Laying: Adult beetles lay their eggs in the soil during the summer months, typically in June and July.
- Hatching: The eggs hatch into larvae (grubs) within a few weeks.
- Feeding: The grubs feed voraciously on grass roots throughout the late summer and early fall. This is when they cause the most damage.
- Overwintering: As temperatures drop, the grubs burrow deeper into the soil to overwinter.
- Pupation: In the spring, the grubs move closer to the surface and pupate.
- Emergence: The pupae transform into adult beetles, which emerge from the soil to mate and begin the cycle anew.
Managing Grub Infestations
There are several strategies for managing grub infestations, ranging from preventative measures to curative treatments. The best approach will depend on the severity of the infestation and your personal preferences.
Preventative Measures
Preventing a grub infestation is often easier than treating one. Consider these preventative measures:
- Healthy Lawn Care Practices: Maintain a healthy lawn through proper watering, fertilization, and mowing. A strong, healthy lawn is more resilient to grub damage.
- Nematodes: Beneficial nematodes are microscopic worms that parasitize grubs. Applying nematodes to your lawn can help control grub populations naturally.
- Milky Spore: Milky spore is a naturally occurring bacterium that infects Japanese beetle grubs. While effective, it may take several years to establish in the soil.
- Timing is Key: Applying preventative treatments at the right time of year (typically in late spring or early summer) can prevent grubs from establishing in your lawn.
Curative Treatments
If you already have a grub infestation, you’ll need to take curative measures to eliminate the pests. Common curative treatments include:
- Insecticides: Several insecticides are effective against grubs, including those containing active ingredients like trichlorfon, carbaryl, and imidacloprid. Always follow the label instructions carefully when applying insecticides.
- Timing is Crucial: Apply curative treatments when the grubs are actively feeding near the surface, typically in late summer or early fall.
- Watering: After applying an insecticide, water your lawn thoroughly to help the product penetrate the soil and reach the grubs.
Choosing the Right Treatment
Selecting the appropriate grub treatment depends on several factors, including the type of grub, the severity of the infestation, and your environmental concerns. Consider the following:
- Identify the Grub Species: Different grub species may respond differently to various treatments. Identifying the specific grub infesting your lawn can help you choose the most effective product.
- Severity of the Infestation: For minor infestations, preventative measures or natural treatments may suffice. Severe infestations may require the use of insecticides.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the potential environmental impact of the treatment. Opt for environmentally friendly options whenever possible.
- Professional Advice: Consult with a lawn care professional for personalized recommendations and treatment plans.
Long-Term Lawn Health
Managing grub bugs is an ongoing process that requires a proactive approach. By implementing preventative measures, monitoring your lawn for signs of infestation, and taking prompt action when necessary, you can protect your lawn from grub damage and maintain a healthy, vibrant landscape. Remember that a healthy, well-maintained lawn is the best defense against grub infestations and other lawn pests. [See also: Lawn Care Tips for Beginners]. Addressing grub bugs life cycle effectively is essential for any homeowner serious about lawn health.
The Role of Soil Health
Healthy soil is the foundation of a healthy lawn. Soil that is rich in organic matter, well-drained, and properly aerated is more resistant to pests and diseases, including grub infestations. Consider these tips for improving soil health:
- Amend the Soil: Add compost or other organic matter to improve soil structure and fertility.
- Aerate the Soil: Aeration helps improve drainage and allows air and water to reach the roots of the grass.
- Test the Soil: Conduct a soil test to determine the pH level and nutrient content of your soil. Amend the soil as needed based on the test results.
Watering Practices
Proper watering is essential for maintaining a healthy lawn and preventing grub infestations. Overwatering can create a favorable environment for grubs, while underwatering can weaken the grass and make it more susceptible to damage. Follow these watering tips:
- Water Deeply and Infrequently: Water your lawn deeply and infrequently, rather than shallowly and frequently. This encourages deep root growth, which makes the grass more resilient to grub damage.
- Water in the Morning: Water your lawn in the morning to allow the grass to dry before nightfall. This helps prevent fungal diseases.
- Avoid Overwatering: Avoid overwatering your lawn, as this can create a moist environment that attracts grubs.
Fertilization
Proper fertilization is crucial for maintaining a healthy lawn and preventing grub infestations. A well-fertilized lawn is more resistant to pests and diseases, including grub damage. Consider these fertilization tips:
- Use a Balanced Fertilizer: Use a balanced fertilizer that contains nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Fertilize at the Right Time: Fertilize your lawn in the spring and fall, when the grass is actively growing.
- Follow the Label Instructions: Follow the label instructions carefully when applying fertilizer.
Conclusion
Dealing with “grub bugs life” can be a challenge, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can effectively manage these pests and maintain a healthy, beautiful lawn. By understanding the grub bugs life cycle, identifying signs of infestation, and implementing preventative and curative measures, you can protect your lawn from grub damage. Remember to prioritize healthy lawn care practices, choose appropriate treatments, and consult with a lawn care professional when needed. With a proactive approach, you can ensure that your lawn remains lush, green, and grub-free for years to come. Don’t let these grub bugs ruin your lawn! Understanding and managing them is crucial for a healthy lawn. Keep in mind the grub bugs life cycle when planning your lawn care strategy. [See also: Choosing the Right Grass Seed]. The key to successful grub control lies in understanding the grub bugs life and acting accordingly.
